Reference
According to a recent research study, food shortages and malnutrition induced by climate change can affect the composition of the 'human gut microbiota'.
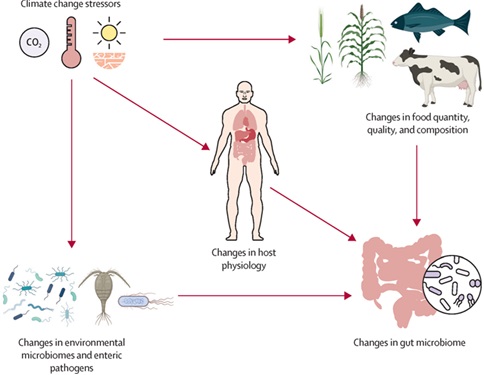
About Gut Microbiota
- Introduction: It is a group of 100 trillion bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses in the gut that affect health.
- Role in Health: Immunity, Metabolism and Glucose Control
Research Findings
- Food Production: High temperatures and CO2 levels are reducing nutrients (protein, zinc, iron etc.) in crops (wheat, maize, rice).
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition has increased in low and middle income countries, which has reduced the diversity (different types of microorganisms) of gut microbiota.
- Disease risk: diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease and neurological disorders (brain related diseases)
- Indigenous communities: dependent on local food sources, higher microbial diversity, more affected by climate change
Environmental factors
- Water and soil: Climate change changes water and soil microbiota, which indirectly affects gut microbiota.
- Heat effect: Food and waterborne diseases increase in hot weather.
- Dysbiosis: Health risk due to imbalance in gut microbiota.